In the First Tier Tribunal case of Grange Road Car Sales one of the main issues was the evidence required to satisfy HMRC that goods have actually left the UK (and, as exports, be zero rated). If a business cannot satisfy HMRC then the sales must be standard rated. There are different levels of evidence required for different types of export, and this case is a handy reminder of the importance of having the correct documentation. I have briefly set out below the different requirements and would strongly advise that any business that exports, regularly or occasionally, to keep this situation under constant review. It is an area which is easy for HMRC to “pick off” transactions and to be “unsatisfied”…
The case
In this case the supplier of cars was based in Northern Ireland and purportedly exported cars to the Republic of Ireland. The purchasers were said to drive the cars over the land boundary. In brief, the appeal was thrown out because both the evidence given in court and the documentation provided appears to have been woefully lacking; which is putting it politely. The case makes entertaining reading (if reading about VAT cases is your thing!). However, it does raise a serious point about exports.
An overview of export requirements
These requirements for exports are set out in Public Notice 703 (although in this case, as the supply was said to be intra-EU, the rules are set out in Public Notice 725). Not only are the requirements prescribed in detail, but they have the force of law (unlike a lot of HMRC’s published Notices). Unless these conditions are met, it is not possible to treat an export as zero rated, even if a business knows that the goods have physically left the UK.
Proof of export
The section of the Notice covering evidence is mainly set out in paragraph 6.
Official evidence
Official evidence is produced by Customs systems, for example Goods Departed Messages (GDM) generated by NES.
Commercial transport evidence
This describes the physical movement of the goods, for example:
- Authenticated sea-waybills
- Authenticated air-waybills
- PIM/PIEX International consignment notes
- Master air-waybills or bills of lading
- Certificates of shipment containing the full details of the consignment and how it left the EC, or
- International Consignment Note/Lettre de Voiture International (CMR) fully completed by the consignor, the haulier and the receiving consignee, or Freight Transport Association own account transport documents fully completed and signed by the receiving customer
Photocopy certificates of shipment are not normally acceptable as evidence of export, nor are photocopy bills of lading, sea-waybills or air-waybills (unless authenticated by the shipping or airline).
Supplementary evidence
You are likely to hold, within your accounting system some, or all, of the following:
- customer’s order
- sales contract
- inter-company correspondence
- copy of export sales invoice
- advice note
- consignment note
- packing list
- insurance and freight charges documentation
- evidence of payment, and/or
- evidence of the receipt of the goods abroad.
You must hold sufficient evidence to prove that a transaction has taken place, though it will probably not be necessary for you to hold all of the items listed.
What must be shown on export evidence?
- The evidence you obtain as proof of export, whether official or commercial, or supporting must clearly identify:
- the supplier
- the consignor (where different from the supplier)
- the customer
- the goods
- an accurate value
- the export destination, and
- the mode of transport and route of the export movement
Vague descriptions of goods, quantities or values are not acceptable. An accurate value, for example; £50,000 must be shown and not excluded or replaced by a lower or higher amount.
How long must I retain export documentation?
To substantiate zero-rating a transaction you must make sure that the proof of export is:
- kept for six years, and
- made readily available to any visiting VAT Officer to substantiate the zero-rating of your exports
What happens if I do not hold the correct export evidence?
If you do not hold the correct export evidence, within the appropriate time limits, then the goods supplied become subject to VAT at the appropriate UK rate.
Additional, or different, evidence is required in the following cases:
- The supply is to a recipient in the EU
- Where the supplier does not arrange shipment of the goods
- Where an overseas customer arranges his own export
- Merchandise in baggage (MIB)
- Groupage or consolidation transactions
- Postal exports
- Exports by courier and fast parcel services
- Exports by rail
- Exports through packers
- Exports through auctioneers
- Exports from Customs, Excise and/or Fiscal warehouses
- Supplies to the Foreign and Commonwealth Office
- Exports to the Channel Islands
This list is not exhaustive.
Summary
As may be seen, there is a degree of complexity here, and curiously, just waving a car off to a different country does not create, in itself, a zero rated export.
We are able to review a business’ export procedures to ensure that, as far as possible, HMRC is satisfied that goods have left the UK and that the correct documentation is held to evidence this.
Please contact us if this service is of interest.

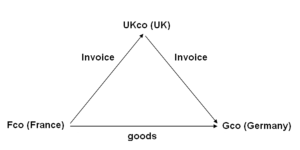 In this example; a UK company (UKco) receives an order from a customer in Germany (Gco). To fulfil the order the UK supplier orders goods from its supplier in France (Fco). The goods are delivered from France to Germany.
In this example; a UK company (UKco) receives an order from a customer in Germany (Gco). To fulfil the order the UK supplier orders goods from its supplier in France (Fco). The goods are delivered from France to Germany.