I have to charge MYSELF VAT?!
How comes?!
Well, normally, the supplier is the person who must account to the tax authorities for any VAT due on the supply. However, in certain situations, the position is reversed and it is the customer who must account for any VAT due. Don’t get caught out!
Here are just some of the situations when you have to charge yourself VAT:
Purchasing services from abroad
These will be obtained free of VAT from an overseas supplier. What is known as the ‘reverse charge’ procedure must be applied. Where the reverse charge procedure applies, the recipient of the services must act as both the supplier and the recipient of the services. On the same VAT return, the recipient must account for output tax, calculated on the full value of the supply received, and (subject to partial exemption and non-business rules) include the VAT charged as input tax. The effect of the provisions is that the reverse charge has no net cost to the recipient if he can attribute the input tax to taxable supplies and can therefore reclaim it in full. If he cannot, the effect is to put him in the same position as if had received the supply from a UK supplier rather than from one outside the UK. Thus creating a level playing field between purchasing from the UK and overseas.
Accounting for VAT and recovery of input tax.
Where the reverse charge procedure applies, the recipient of the services must act as both the supplier and the recipient of the services. On the same VAT return, the recipient must
-
-
-
account for output tax, calculated on the full value of the supply received, in Box 1;
-
(subject to partial exemption and non-business rules) include the VAT stated in box 1 as input tax in Box 4; and;
-
include the full value of the supply in both Boxes 6 and 7.
-
-
Value of supply: The value of the deemed supply is to be taken to be the consideration in money for which the services were in fact supplied or, where the consideration did not consist or not wholly consist of money, such amount in money as is equivalent to that consideration. The consideration payable to the overseas supplier for the services excludes UK VAT but includes any taxes levied abroad.
Time of supply: The time of supply of such services is the date the supplies are paid for or, if the consideration is not in money, the last day of the VAT period in which the services are performed.
Purchasing goods from another EC Member States
Something similar to reverse charge; called acquisition tax, applies to goods purchased from other EC Member States. These are known as acquisitions (they are imports if the goods come from outside the EC and different rules apply). The full value of the goods is subject to output tax and the associated input tax may be recovered by the business acquiring if the goods are used for taxable purposes. If you‘re not already registered for VAT in the UK and acquire goods worth £82,000 or more in the UK from other EC countries, you will have to register for VAT in the UK on the strength of the value of the acquisition tax. A business will also have to complete an Intrastat Supplementary Declaration (SDs) if its acquisitions of goods from the EC exceed an annual amount – currently £1.5 million.
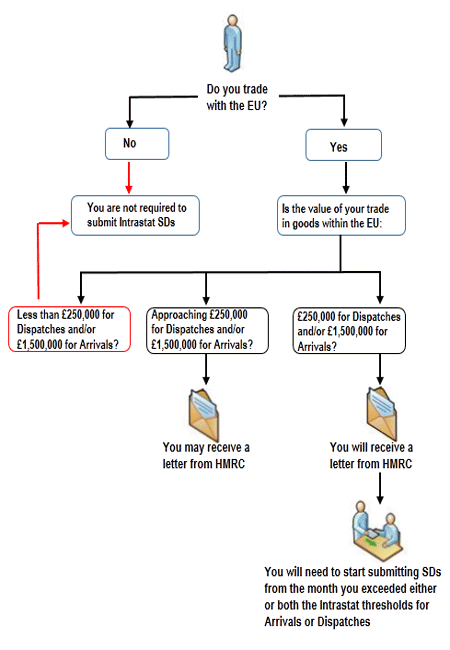 More details on Intrastat Supplementary Declarations here
More details on Intrastat Supplementary Declarations here
Deregistration
Any goods on hand at deregistration with a total value of over £1,000 on which input tax has been claimed are subject to a self supply. This is a similar mechanism to a reverse charge in that the goods are deemed to be supplied to the business by the business and output tax is due. However, in these circumstances it is not possible to recover any input tax on the self supply.
Flat Rate Scheme
There is a self supply of capital items on which input tax has been claimed when a business leaves the flat rate scheme (and remains VAT registered).
Mobile telephones
In order to counter missing trader intra-community fraud (‘MTIC’), supplies of mobile ‘phones and computer chips which are made by one VAT registered business to another and valued at £5,000 and over are subject to the reverse charge. This means that the purchaser rather than the seller is responsible for accounting for VAT due.
Land and buildings…. and motor cars
There are certain circumstances where land and buildings must be treated as a self supply… but that is a whole new subject in itself… as is supplies in the motor trade.
Even if the result of a self-supply or reverse charge is VAT neutral HMRC is within its rights to assess and levy penalties and interest in cases where the charge has not been applied; which always seems unfair. However, more often than not simple accounting entries will deal with the matter…. if the circumstances are recognised and it is remembered to actually make the entries!
